In today's mobile-dominated world, website performance can make or break user experience. With over 60% of web traffic coming from mobile devices, learning how to reduce filesize mobile content has become essential for website owners and developers. Mobile users expect fast-loading pages, and heavy file sizes can lead to slow load times, frustrated visitors, and higher bounce rates. This guide will walk you through practical strategies to optimize your website's files for mobile users, ensuring a smooth and speedy experience across all devices.

Why Mobile File Size Optimization Matters
Mobile users face unique challenges compared to desktop users. They often rely on cellular data connections that can be slower and less reliable than Wi-Fi. Large file sizes consume more data, which costs users money and patience. According to web performance research, 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than three seconds to load.
Search engines like Google also prioritize mobile-friendly websites in their rankings. The mobile-first indexing approach means Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for ranking purposes. If your mobile pages load slowly due to large file sizes, your search engine rankings will suffer. Optimizing file sizes directly impacts your visibility, traffic, and ultimately, your bottom line.
Key Takeaways:
- Mobile users represent over 60% of web traffic and expect fast-loading pages
- Large file sizes lead to slow load times, higher bounce rates, and poor user experience
- Mobile optimization directly impacts search engine rankings and visibility
- Reducing file sizes saves users data and improves accessibility across all connection types
Effective Strategies to Reduce Filesize Mobile Content
Image Optimization Techniques
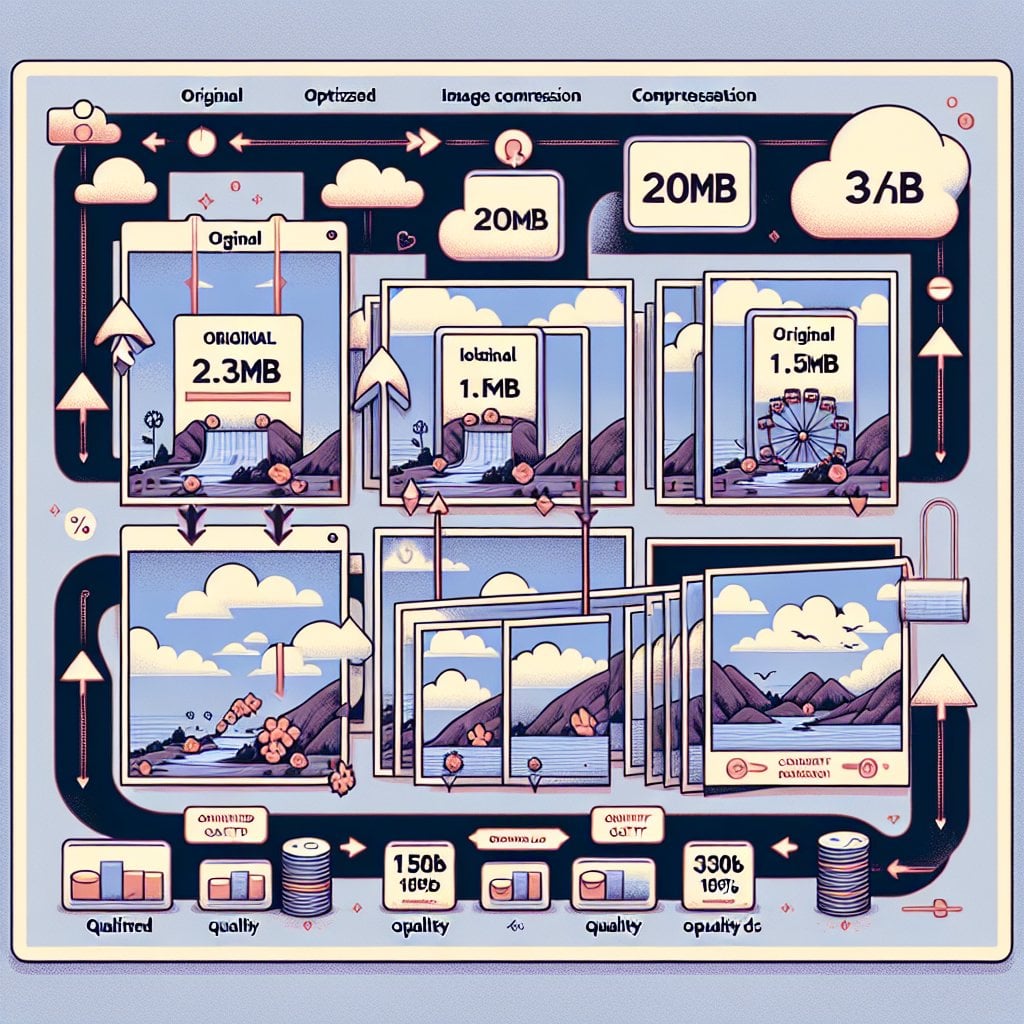
Images typically account for the largest portion of page weight. Optimizing them is the most impactful way to reduce filesize mobile pages experience. Start by choosing the right file format. Use JPEG for photographs, PNG for images requiring transparency, and consider modern formats like WebP, which offers superior compression without sacrificing quality.
Compress your images before uploading them to your website. Tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or built-in CMS compression features can reduce file sizes by 50-80% without noticeable quality loss. Always resize images to match their display dimensions. If an image displays at 800 pixels wide on mobile, don't upload a 3000-pixel version.
Implement responsive images using the srcset attribute in your HTML code. This technique serves different image sizes based on the user's screen size and resolution. Mobile users receive smaller files while desktop users get higher resolution images when needed.
Minifying Code and Resources
Your website's HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files contain unnecessary characters like spaces, line breaks, and comments that increase file size. Minification removes these elements without affecting functionality. Most modern build tools and content management systems offer automatic minification options.
Combine multiple CSS and JavaScript files into single files when possible. Each separate file requires an additional HTTP request, which adds loading time. Fewer requests mean faster page loads, especially on mobile networks where latency is higher. Consider using critical CSS techniques, which inline essential styles needed for above-the-fold content while deferring the rest.
Leveraging Browser Caching and Compression
Enable GZIP or Brotli compression on your web server. These compression methods can reduce file sizes by up to 70% during transmission. Most modern servers support these features, and they work transparently for users. Check with your hosting provider or server administrator to ensure compression is enabled.
Configure browser caching to store static resources locally on users' devices. When visitors return to your site, their browser loads cached files instead of downloading them again. This dramatically improves load times for returning visitors and reduces bandwidth consumption.
Advanced Mobile Optimization Tactics
Lazy Loading Implementation
Lazy loading defers the loading of images and other resources until they're needed. Instead of loading all images when the page opens, lazy loading only loads images as users scroll down. This technique significantly reduces initial page load times and saves data for users who don't scroll through entire pages.
Modern browsers support native lazy loading through the loading="lazy" attribute on image tags. For broader compatibility and more control, JavaScript libraries like Intersection Observer API provide robust lazy loading solutions. Apply lazy loading to images, videos, and even iframe embeds to maximize performance gains.
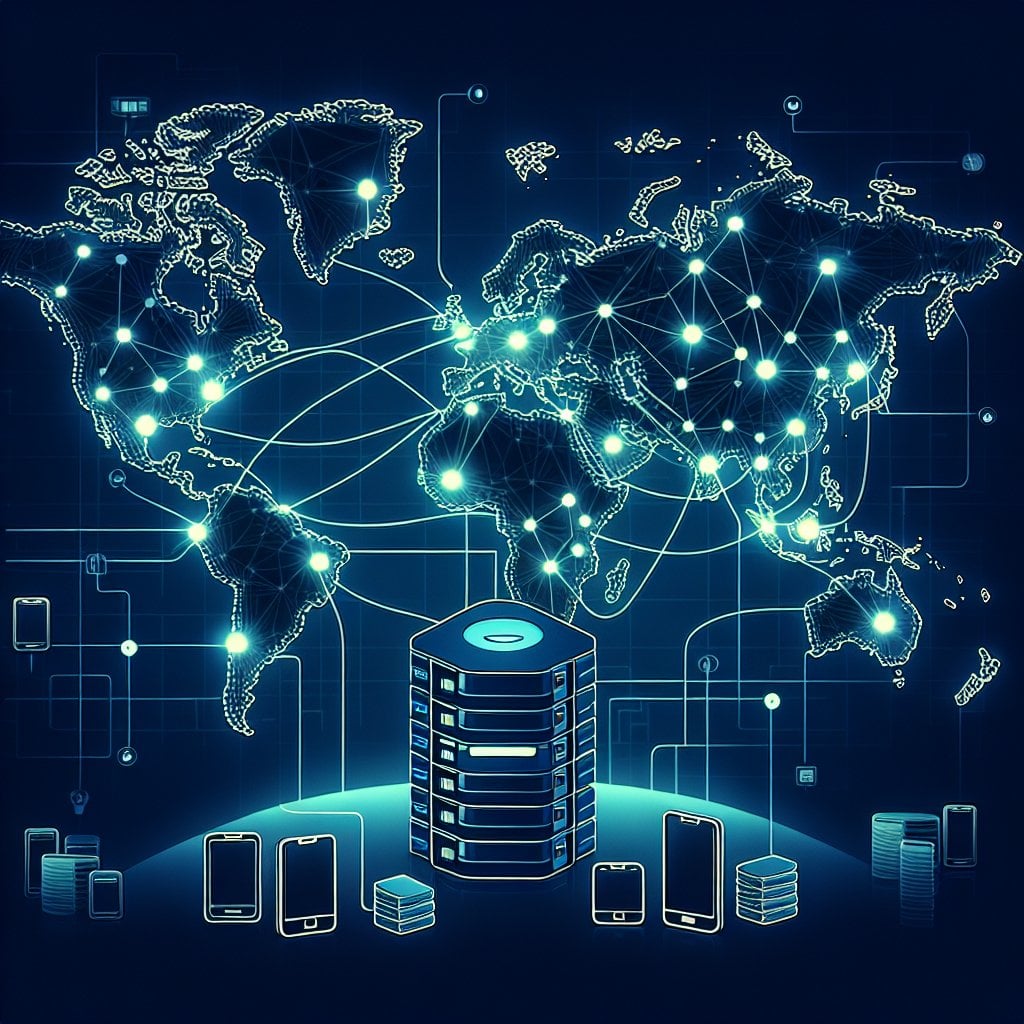
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A Content Delivery Network distributes your website's files across multiple servers worldwide. When mobile users access your site, they receive files from the server closest to their location, reducing latency and improving load times. Many CDNs also offer automatic image optimization and compression features.
Popular CDN providers include Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, and Fastly. Many offer free tiers suitable for small to medium-sized websites. Setting up a CDN typically involves updating your DNS settings and configuring caching rules for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Optimizing file sizes for mobile users is no longer optional in today's mobile-first world. By implementing image optimization, code minification, compression techniques, and advanced strategies like lazy loading and CDNs, you can dramatically improve your website's mobile performance. Remember that every kilobyte matters when users are on cellular connections. Start with the biggest impact items like images, then progressively implement other optimizations. Regular testing on real mobile devices and connections will help you identify areas for improvement and ensure your mobile users enjoy fast, smooth experiences that keep them engaged with your content.
FAQ
Ideally, mobile web pages should be under 1-2 MB total, including all images, scripts, and stylesheets. Pages under 500 KB load fastest and provide the best user experience on cellular connections. Google recommends keeping critical resources under 14 KB for optimal initial rendering.
Proper image compression can reduce file sizes by 50-80% without noticeable quality loss. Using modern formats like WebP can achieve even greater compression rates, sometimes up to 90% smaller than original files while maintaining visual quality suitable for mobile displays.
When done correctly, file size reduction has minimal impact on perceived quality on mobile screens. Mobile displays are smaller and have different viewing conditions than desktop monitors, so moderate compression is rarely noticeable. The key is finding the right balance between file size and quality for your specific images.
Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest are excellent free tools for measuring mobile performance. These tools analyze your page load times, identify large files, and provide specific recommendations for optimization. Chrome DevTools also offers mobile device emulation for testing during development.
Modern best practice favors responsive design with a single codebase that adapts to different screen sizes. Using responsive images and mobile-first CSS, you can serve appropriately sized resources to each device type without maintaining separate versions. This approach is easier to maintain and aligns with Google's mobile-first indexing.